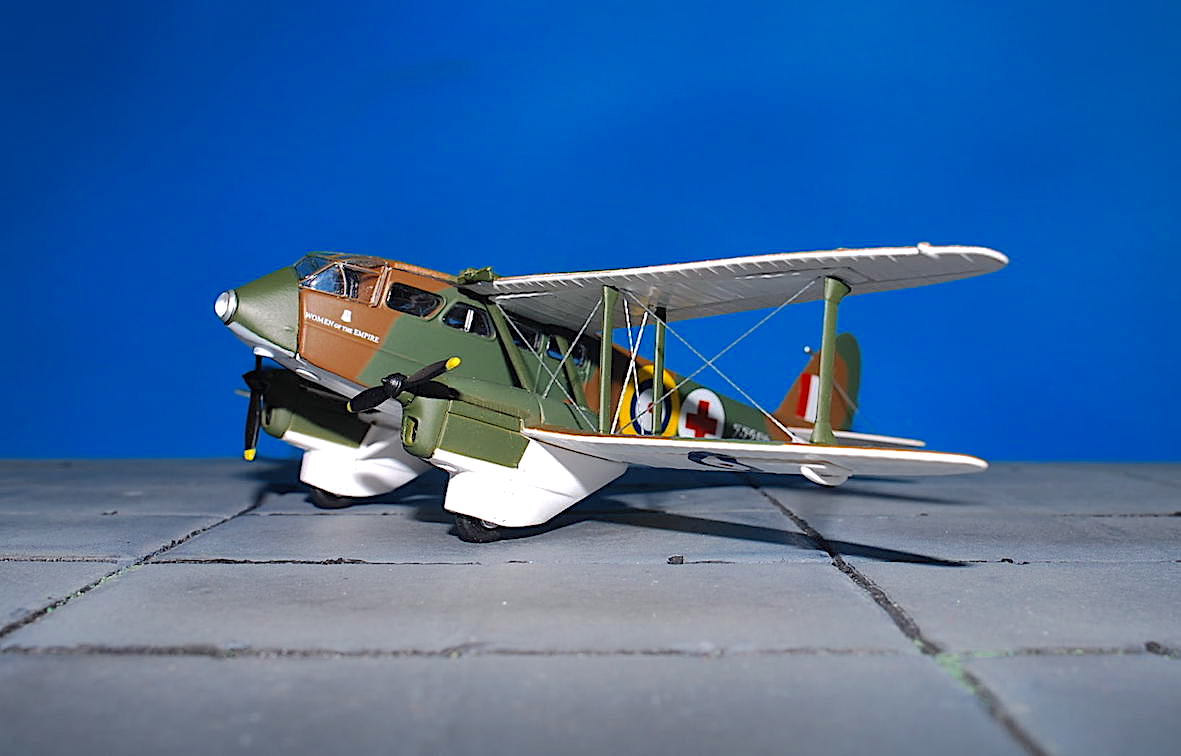
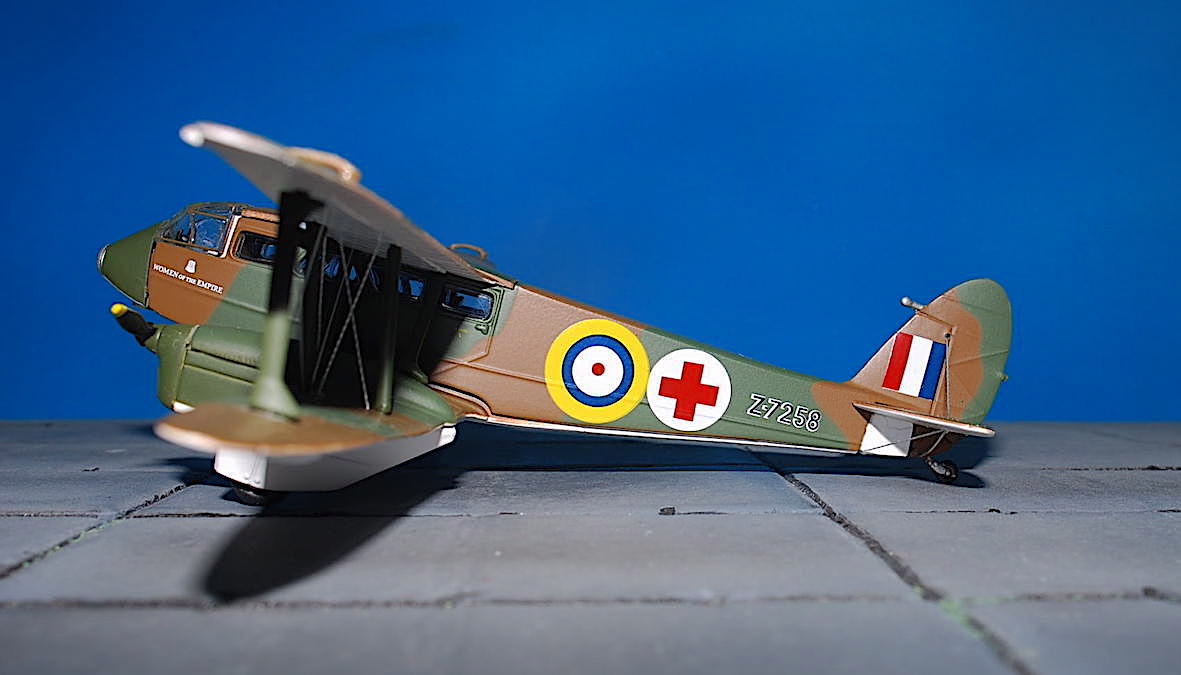
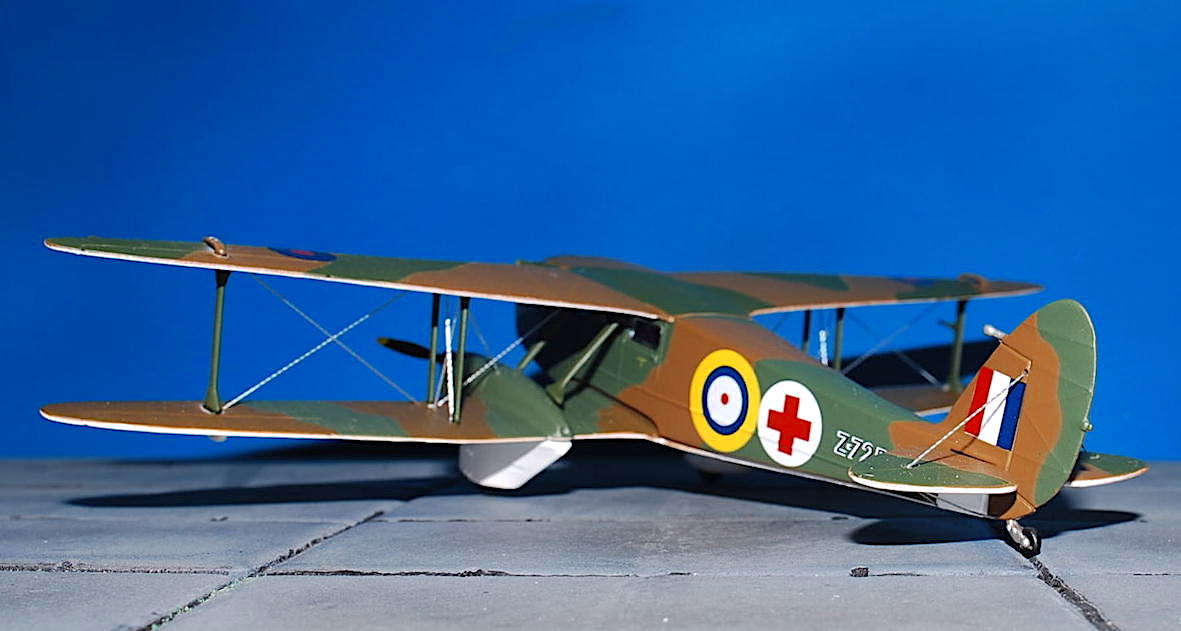
Oxford – de Havilland D.H.89 Dragon Rapide , ‚Z-7258/G-AFMH‘ RAF Air Ambulance
1,199 Kč
Není skladem
Výrobce: Oxford DiecastMěřítko: 1:72Letecká společnost: RAF - Royal Air ForcePopis
-sběratelský model letadla de Havilland D.H.89 Dragon Rapide 1/72 -provedení: kovový model s plastovými částmi -model je v kvalitním provedení
de Havilland D.H.89 Dragon Rapide
De Havilland DH.89 Dragon Rapide byl britský dopravní letoun pro krátké tratě z 30. let 20. století. Byl navržený na konci roku 1933 jako rychlejší a pohodlnější nástupce letounu DH.84 Dragon a v zásadě se jednalo o dvoumotorovou, zmenšenou verzi čtyřmotorového letounu DH.86 Express. Se svým větším bratříčkem sdílel mnoho společných prvků včetně zužujících se křídel, aerodynamičtějších tvarů a motorů Gipsy Six. Na druhou stranu ale nezdědil žádnou z letových nectností většího letounu a stal se tak jedním z nejúspěšnějších britských dopravních letounů 30. let.
The de Havilland DH.89 Dragon Rapide was a 1930s short-haul biplane airliner developed and produced by British aircraft company de Havilland. Capable of accommodating 6–8 passengers, it proved an economical and durable craft, despite its relatively primitive plywood construction.Developed during the early 1930s, the Dragon Rapide was essentially a smaller, twin-engined version of the four-engined DH.86 Express, and shared a number of common features, such as its tapered wings, streamlined fairings and Gipsy Six engines. First named the „Dragon Six“, the type was marketed as „Dragon Rapide“ and later simply known as the „Rapide“. Upon its introduction in summer 1934, it proved to be a popular aircraft with airlines and private civil operators alike, attaining considerable foreign sales in addition to its domestic use.
| Role | Short-haul airliner |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | de Havilland |
| First flight | 17 April 1934 |
| Primary user | Royal Air Force |
| Number built | 727 |
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Capacity: 8 passengers
- Length: 34 ft 6 in (10.5 m)
- Wingspan: 48 ft 0 in (14.6 m)
- Height: 10 ft 3 in (3.1 m)
- Wing area: 340 ft² (32 m²)
- Empty weight: 3,230 lb (1,460 kg)
- Loaded weight: 5,500 lb (2,490 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × de Havilland Gipsy Six inline engine, 200 hp (149 kW) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 157 mph (136 kn, 253 km/h) at 1,000 ft (305 m)
- Range: 573 mi (498 nmi, 920 km)
- Service ceiling: 16,700 ft (5,090 m)
- Rate of climb: 867 ft/min (4.3 m/s)
- Wing loading: 16 lb/ft² (79 kg/m²)
- Power/mass: 0.073 hp/lb (120 W/kg)
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom’s aerial warfare force. Formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918,it is the oldest independent air force in the world. Following victory over the Central Powers in 1918 the RAF emerged as, at the time, the largest air force in the world. Since its formation, the RAF has taken a significant role in British military history. In particular, it played a large part in the Second World War where it fought its most famous campaign, the Battle of Britain.
| Royal Air Force | |
|---|---|

Badge of the Royal Air Force
|
|
| Founded | 1 April 1918 |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Type | Air force |
| Role | Aerial warfare |
| Size | 33,840 active personnel 832 operational aircraft 1,940 RAuxAF 2,220 reserve personnel |
| Part of | British Armed Forces |
| Air Staff Offices | Whitehall, London |
| Motto(s) | Latin: Per Ardua ad Astra “Through Adversity to the Stars” |
| March | Royal Air Force March Past |
| Commanders | |
| Chief of the Air Staff | Air Chief Marshal Mike Wigston |
| Notable commanders |
Lord Trenchard Lord Portal |
| Insignia | |
| Ensign |
 |
| Logo |
 |
| Roundels |   |
| Fin flashes |   |
| Pilot’s brevet |  |
| Aircraft flown | |
| Attack | |
| Fighter | |
| Trainer helicopter | |
| Utility helicopter | |
| Reconnaissance |
|
| Trainer |
|
| Transport |
|
Další informace
| Výrobce | |
|---|---|
| Měřítko | |
| Letecké společnosti |